Our Research
The fourth division (BP4) of The Fundamental Research Department (Departament Badań Podstawowych) deals with research in astrophysics and astronomy, mainly their observational aspects. The BP4 division is located in Warsaw at 7 Pasteura street.
The research conducted at the Astrophysics Laboratory includes:
- Cosmology: CMB, large structures of the Universe, dark matter, non-standard cosmology and gravitational lensing
- Gravitational waves: Multi-messenger astronomy, new tools for cosmology
- Physics of galaxies: Formation and evolution of galaxies, AGN, quasars and gamma-ray burst
- Interstellar medium: Star formation, neutron stars and white dwarfs
The BP4 division is also involved in several international projects. Check our Scientific Projects page for more information.
Seminars
Upcoming seminars for all of NCBJ can be found here.
The seminar archive for NCBJ can be found here.
Latest News
Scroll down for the latest news about the research done by our division or click here.
World News
dr Pratik Dabhade from BP4 was a leading author in a recent paper studying odd radio circles. The paper, published in MNRAS, found an extremely rare double-ringed odd radio circle. This has created a stir around the world, attracting the attention of CNN (https://edition.cnn.com/2025/10/14/science/odd-radio-circles-double-rings) and CBS (https://www.cbsnews.com/news/most-powerful-odd-radio-circle-twins-ever-detected/).Conference Participation
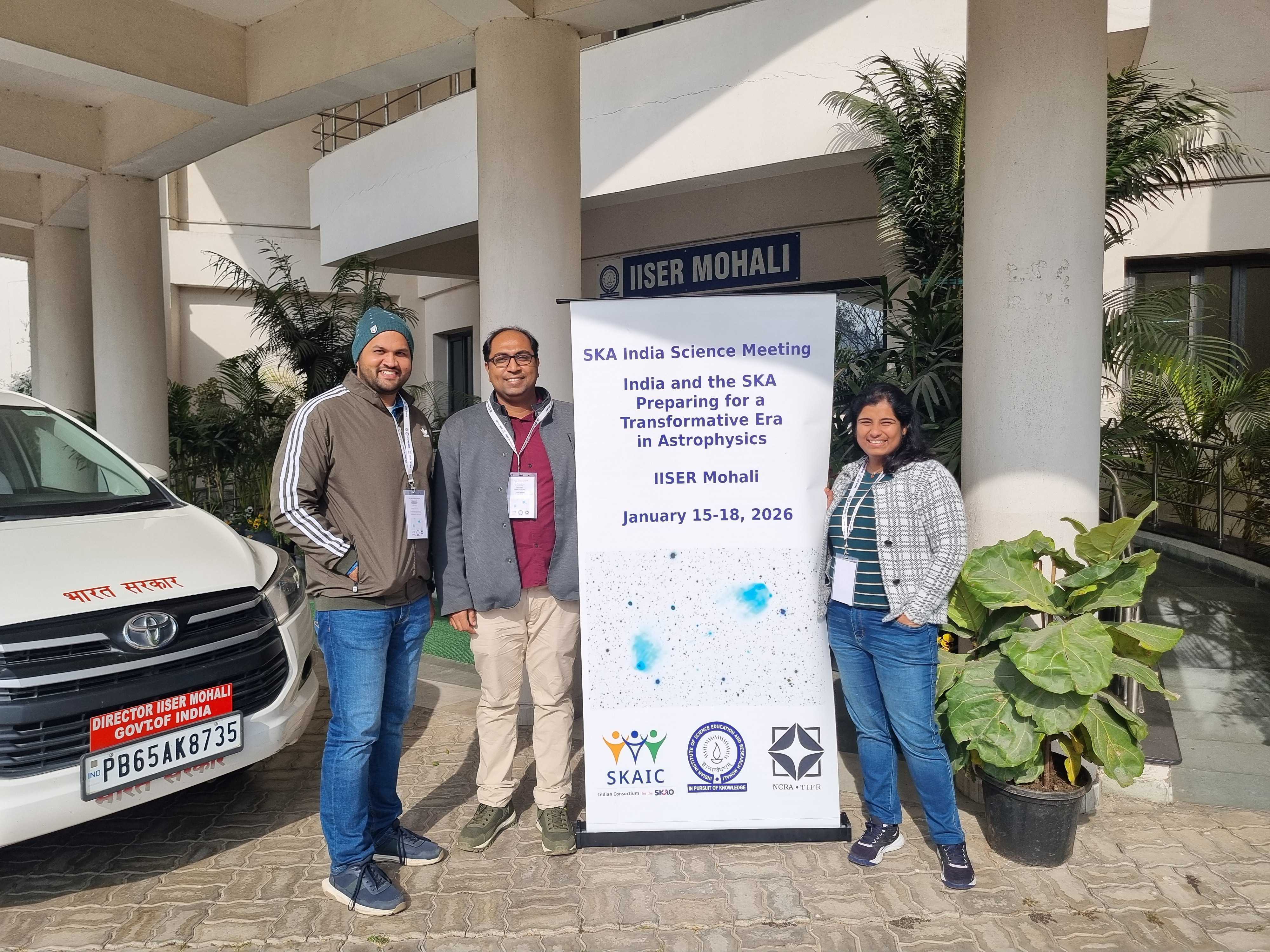
BP4 participate in may national and intersectional conferences. We share our cutting edge research and enthusiasm with other astronomers across the world. Below are pictures from our trips across the globe over the last year or so.
Latest News
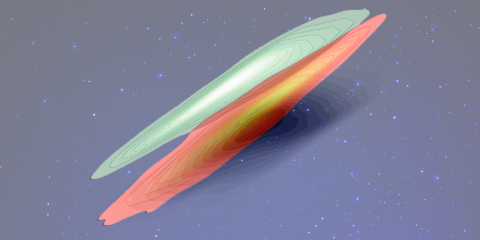
In the Universe, appearance matters: Dusty shapes of colourful galaxies
Can we see what is hidden in a cloud of dust without the aid of infrared vision? Scientists involved in the largest optical survey of the sky this decade, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST), led by a group from the NCBJ’s Astrophysics Division, in a paper published in April in Astronomy & Astrophysics, propose a novel method to extract information about dust in galaxies without actually observing its infrared light.
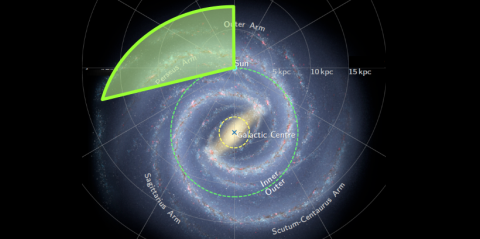
New observations of the outer Milky Way help to understand the star formation process
Having an accurate understanding of the star formation process is essential to comprehend the formation and evolution of galaxies, and this requires to unveil the impact of environment on star formation. In a new study published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, scientists used a new survey of the outer Galaxy to refine the distance and properties of star-forming clumps and study how star formation behave in comparison with the inner Galaxy.

Dr. Michael Romano receives prestigious award from Astronomy & Astrophysics
Dr. Michael Romano, a researcher at the Department of Astrophysics of the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ), has been honored with the prestigious "Early Career Research Award" by the journal "Astronomy & Astrophysics" (A&A). The "Early Career Research Award" is bestowed annually upon young scientists who have demonstrated exceptional accomplishments in the field of astrophysics.

Gas on the run – ALMA spots the shadow of a molecular outflow from a quasar when the Universe was less than one billion years old
Theoretical predictions have been confirmed with the discovery of an outflow of molecular gas from a quasar when the Universe was less than a billion years old. The results obtained from the observations of the ALMA telescope are of great importance for understanding the processes of star formation in galaxies. Dr. Darko Donevski from the NCBJ Astrophysics Division participated in the work of the research team.
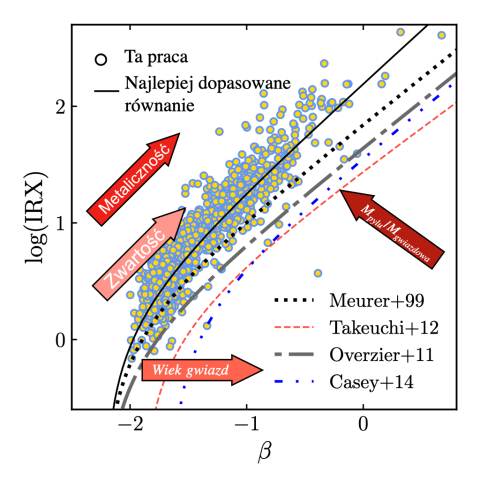
Midlife Crisis of the Universe: Galaxies’ interactions did not affect interstellar dust
A new study has shed light on the intricate cosmic dance between interstellar dust in galaxies, properties of galaxies, and their environments. For a very long time, the relations between dust and the galaxies was investigated. However, the link between dust properties and the neighborhood of galaxies was poorly understood. In the newest work published in Astronomy&Astrophysics, the scientists studied the relationship between the amount of stellar light absorbed by dust, and the environments of galaxies.

Professor Agnieszka Pollo has taken the position of Deputy Director for Science at NCBJ
On October 16, 2023, a change took place in the position of Deputy Director for Science at NCBJ. The former director, Professor Ewa Rondio, passed on her duties to Professor Agnieszka Pollo, an astrophysicist who has been successfully leading the rapidly developing Department of Astrophysics.












