Our Research
The fourth division (BP4) of The Fundamental Research Department (Departament Badań Podstawowych) deals with research in astrophysics and astronomy, mainly their observational aspects. The BP4 division is located in Warsaw at 7 Pasteura street.
The research conducted at the Astrophysics Laboratory includes:
- Cosmology: CMB, large structures of the Universe, dark matter, non-standard cosmology and gravitational lensing
- Gravitational waves: Multi-messenger astronomy, new tools for cosmology
- Physics of galaxies: Formation and evolution of galaxies, AGN, quasars and gamma-ray burst
- Interstellar medium: Star formation, neutron stars and white dwarfs
The BP4 division is also involved in several international projects. Check our Scientific Projects page for more information.
Seminars
Upcoming seminars for all of NCBJ can be found here.
The seminar archive for NCBJ can be found here.
Latest News
Scroll down for the latest news about the research done by our division or click here.
World News
dr Pratik Dabhade from BP4 was a leading author in a recent paper studying odd radio circles. The paper, published in MNRAS, found an extremely rare double-ringed odd radio circle. This has created a stir around the world, attracting the attention of CNN (https://edition.cnn.com/2025/10/14/science/odd-radio-circles-double-rings) and CBS (https://www.cbsnews.com/news/most-powerful-odd-radio-circle-twins-ever-detected/).Conference Participation
BP4 participate in may national and intersectional conferences. We share our cutting edge research and enthusiasm with other astronomers across the world. Below are pictures from our trips across the globe over the last year or so.
Latest News
![Zdjęcie: Artystyczna interpretacja odpływów galaktycznych. Aktywność gwiazdotwórcza może skutkować powstawaniem potężnych wiatrów (odpływów), które są w stanie przenosić gaz na bardzo duże odległości, aż do przestrzeni międzygalaktycznej. Linie emisyjne [CII] 158 μm wyraźnie wskazują na odpływ gazu atomowego. Źródło: ESA/Hubble, ESO/L. Calçada, M. Romano. Zdjęcie: Artystyczna interpretacja odpływów galaktycznych. Aktywność gwiazdotwórcza może skutkować powstawaniem potężnych wiatrów (odpływów), które są w stanie przenosić gaz na bardzo duże odległości, aż do przestrzeni międzygalaktycznej. Linie emisyjne [CII] 158 μm wyraźnie wskazują na odpływ gazu atomowego. Źródło: ESA/Hubble, ESO/L. Calçada, M. Romano.](/sites/default/files/styles/large/public/2023-10/press_image_pol.png?itok=90m0Frbx)
Galactic outflows drive the evolution of dwarf galaxies
Stellar feedback is expected to play a key role in regulating the evolution of low-mass galaxies by producing galactic-scale winds (also known as outflows) that push the gas away from the interstellar medium, eventually preventing from the formation of new stars. In this respect, an international team of astronomers led by NCBJ scientist, have published a work on the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal addressing the impact of galactic outflows on the baryonic cycle of nearby dwarf galaxies

Annual Awards Presented by the Fundamental Research Department of NCBJ
On June 26, 2023, a Special Colloquium was held, during which awards were presented for the best research and popularization activities in 2022 at the Fundamental Research Department. The winners were Prof. Michał Bluj, a team consisting of Prof. Paweł Ziń and Dr. Maciej Pylak, Dr. Michael Romano, and Prof. Jerzy Kowalski-Glikman and Dr. Miguel Figueira
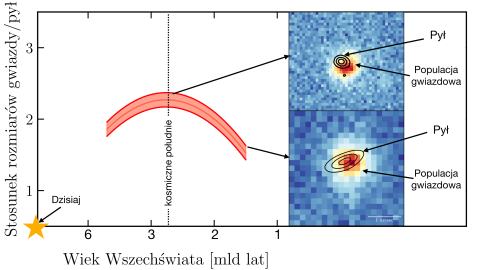
Unveiling the hidden stars: ALMA Shines a Light on Dust Attenuation
Interstellar dust is a key component in galaxies. It favors star formation and drives the chemistry and physics of the interstellar medium. However, it hides the majority of stars in a way that it is impossible to observe them. Astrophysicists use dust attenuation laws that would uncover these hidden stars by reverse-engineering the light from galaxies to quantify how many stars are there.
The project of a PhD student of the NCBJ Department of Astrophysics qualified for the „Pearls of Science” program
The first edition of the competition under the „Pearls of Science” program has been settled. One of the scientists qualified for the program is Krzysztof Lisiecki, MSc, a PhD student at the Astrophysics Department of the National Center for Nuclear Research, conducting research in the project „In search of witnesses to the early Universe – studying the properties of red nuggets”.
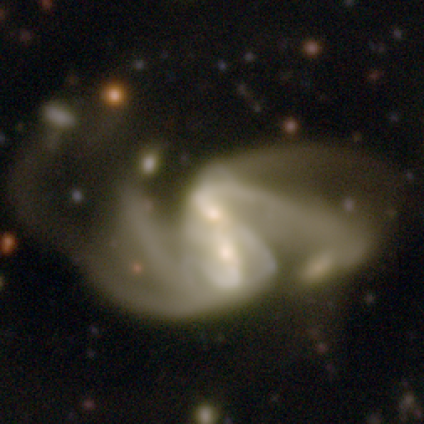

New images of tens of thousands of galaxies have been made available at the Galactic Zoo
Twenty thousand high quality images from the Hawaii Two-0 (H20)/Cosmic Dawn survey have been released to the public on the most popular citizen science project: Galaxy Zoo. Anyone in the world can become a citizen scientist and help astronomers classify images from the Subaru telescope.
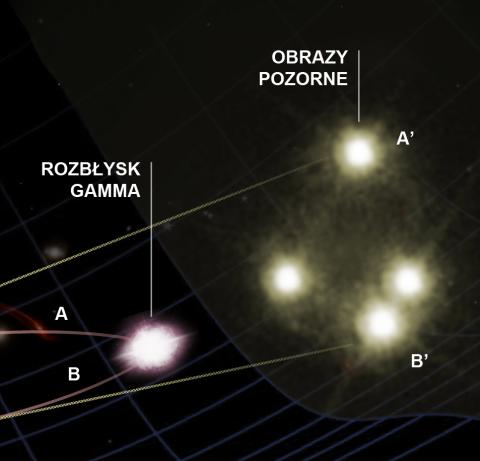
Wyścigi fotonów pod lupą grawitacji
Fotony przemierzają Wszechświat z niezmienną prędkością. Tylko czy zawsze wszystkie z tą samą? Aby sprawdzić, czy potencjalne efekty kwantowej grawitacji nie wpływają na prędkości fotonów o bardzo dużych energiach, polsko-chiński zespół naukowców zaprzągł do pracy dwa spektakularne zjawiska kosmiczne: soczewki grawitacyjne i wybuchy promieniowania gamma.












