Our Research
The fourth division (BP4) of The Fundamental Research Department (Departament Badań Podstawowych) deals with research in astrophysics and astronomy, mainly their observational aspects. The BP4 division is located in Warsaw at 7 Pasteura street.
The research conducted at the Astrophysics Laboratory includes:
- Cosmology: CMB, large structures of the Universe, dark matter, non-standard cosmology and gravitational lensing
- Gravitational waves: Multi-messenger astronomy, new tools for cosmology
- Physics of galaxies: Formation and evolution of galaxies, AGN, quasars and gamma-ray burst
- Interstellar medium: Star formation, neutron stars and white dwarfs
The BP4 division is also involved in several international projects. Check our Scientific Projects page for more information.
Seminars
Upcoming seminars for all of NCBJ can be found here.
The seminar archive for NCBJ can be found here.
Latest News
Scroll down for the latest news about the research done by our division or click here.
World News
dr Pratik Dabhade from BP4 was a leading author in a recent paper studying odd radio circles. The paper, published in MNRAS, found an extremely rare double-ringed odd radio circle. This has created a stir around the world, attracting the attention of CNN (https://edition.cnn.com/2025/10/14/science/odd-radio-circles-double-rings) and CBS (https://www.cbsnews.com/news/most-powerful-odd-radio-circle-twins-ever-detected/).Conference Participation
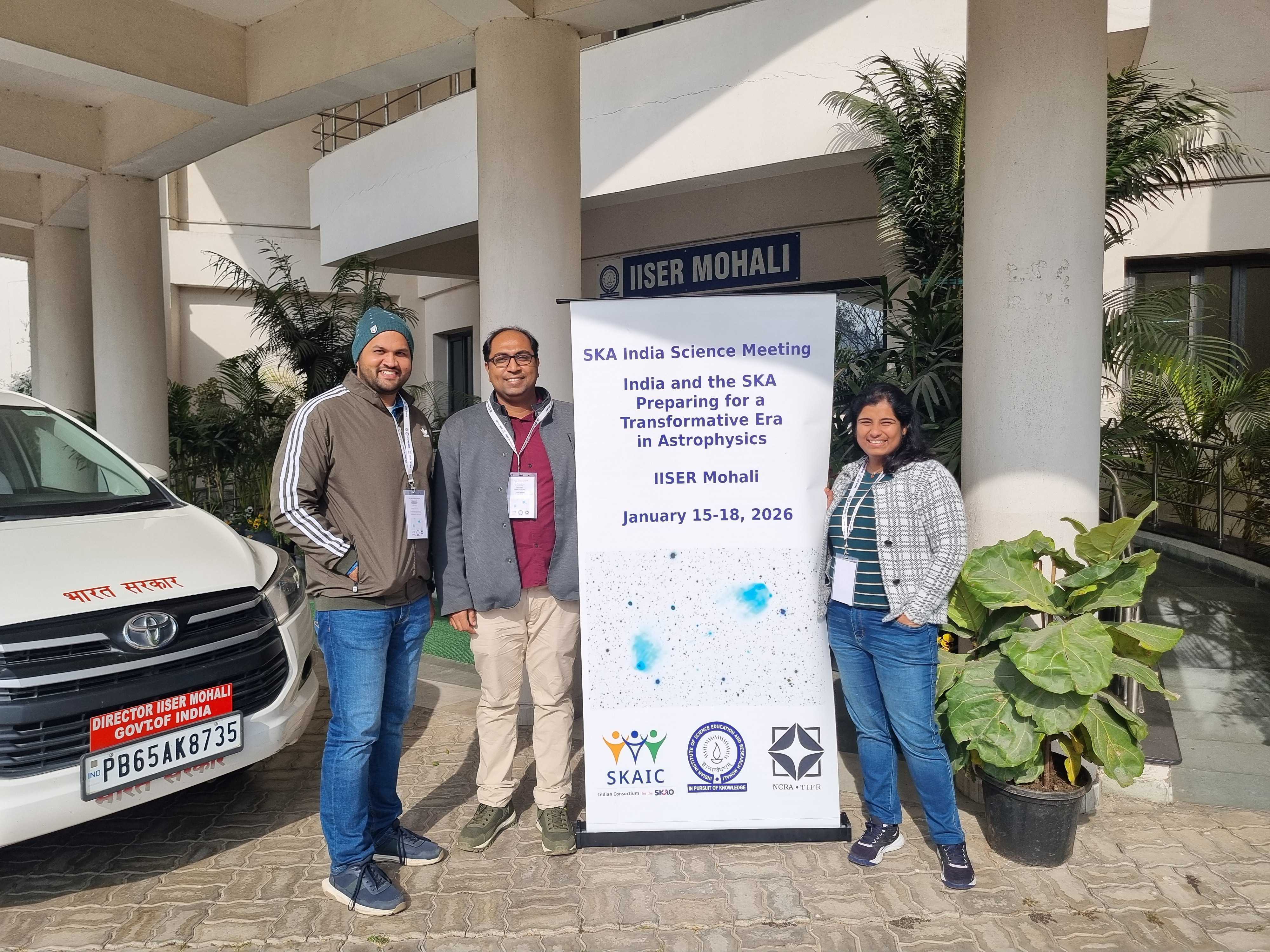
BP4 participate in may national and intersectional conferences. We share our cutting edge research and enthusiasm with other astronomers across the world. Below are pictures from our trips across the globe over the last year or so.
Latest News
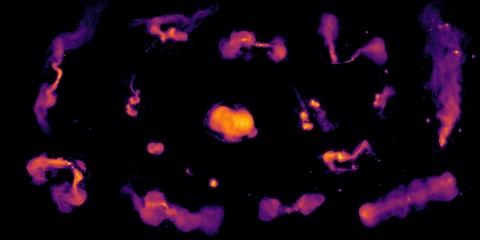
Largest Ever Radio Sky Survey Maps the Universe in Unprecedented Detail
An international collaboration using the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) has unveiled an exceptionally detailed radio sky map, revealing 13.7 million cosmic sources and delivering the most complete census yet of actively growing supermassive black holes. It showcases an extraordinary variety of systems powered by these black holes, whose radio emission can extend for millions of light-years. The newly released LOFAR Two-metre Sky Survey (LoTSS-DR3) marks a major milestone in radio astronomy and international scientific collaboration. The result is published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.

Silent Giants, Hidden Fuel: ALMA Reveals Surprising Diversity of Dust and Gas in Quiescent Galaxies
New ALMA observations reveal that diverse reservoirs of dust and molecular gas can persist long after galaxies stop forming stars, challenging theoretical expectations.

NCBJ joins the European astroparticle physics initiative EuCAPT
A group of researchers from the National Centre for Nuclear Research, in cooperation with scientists from institutes of the Polish Academy of Sciences, has joined the European scientific initiative EuCAPT. The NCBJ is among the first Polish centres to join this international collaboration.
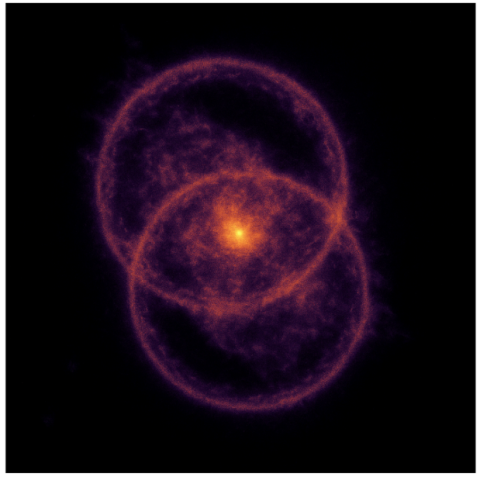

Discovery of the Most Powerful Odd Radio Circle to Date
Astronomers have discovered the most distant and most powerful “odd radio circle” (ORC) ever observed – with key contributions from a researcher at the Astrophysics division of the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ).

NCBJ scientists investigate the origin of carbon dust in one of the oldest known galaxies
A team of researchers from the Astrophysics Division of the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ), led by dr hab. Ambra Nanni, has conducted a pioneering study of the origin of carbon dust in one of the most distant galaxies known to science – JADES–GS-z6-0. Data collected by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has provided new insights into the presence of complex molecules, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), in the early Universe, less than a billion years after the Big Bang.

NCBJ scientists awarded for achievements in fundamental research
During the Special Seminar of the NCBJ's Department of Fundamental Research, the awards of the Department's Director for the greatest scientific achievements of the past year were awarded in accordance with tradition. This time, awards were given for research into the role of dust in the evolution of galaxies, reflections on classical and quantum gravity, and work on symmetry violation in the decay of beauty mesons. The event took place on 30 June.












